on
Short Summary: Learning Data Augmentation Strategies for Object Detection (2019)
Authors: Barret Zoph, Ekin D. Cubuk, Golnaz Ghiasi, Tsung-Yi Lin, Jonathon Shlens, Quoc V. Le
Link to paper: [https://arxiv.org/pdf/1906.11172.pdf)
Problem
2D-Detection
Improvement over previous methods
- Better mAP.
- No manual data augmentation.
Method
There are three kinds of data augmentation for object detection: image transformations that leave the position of the bounding boxes unchanged, image transformations that change the position of the bounding boxes, but not relative to the image (e.g. rotation) and transformations that are applied within the bounding boxes only. They identify 22 operations that are beneficial for object detection. Their goal is to find a data augmentation policy that randomly applies one of 5 sub-policies. Each sub-policy consists of 2 operations in sequence. Each operation is applied with a probability and magnitude, both discretized in 6 uniformly spaced values. Therefore, they need to search over a subspace of cardinality of size $(22LM)^2$ for each sub-policy and over a space of cardinality of size $(22 \times 6 \times 6)^{2 \times 5} \approx 9.6 \times 1028$ for the full policy.
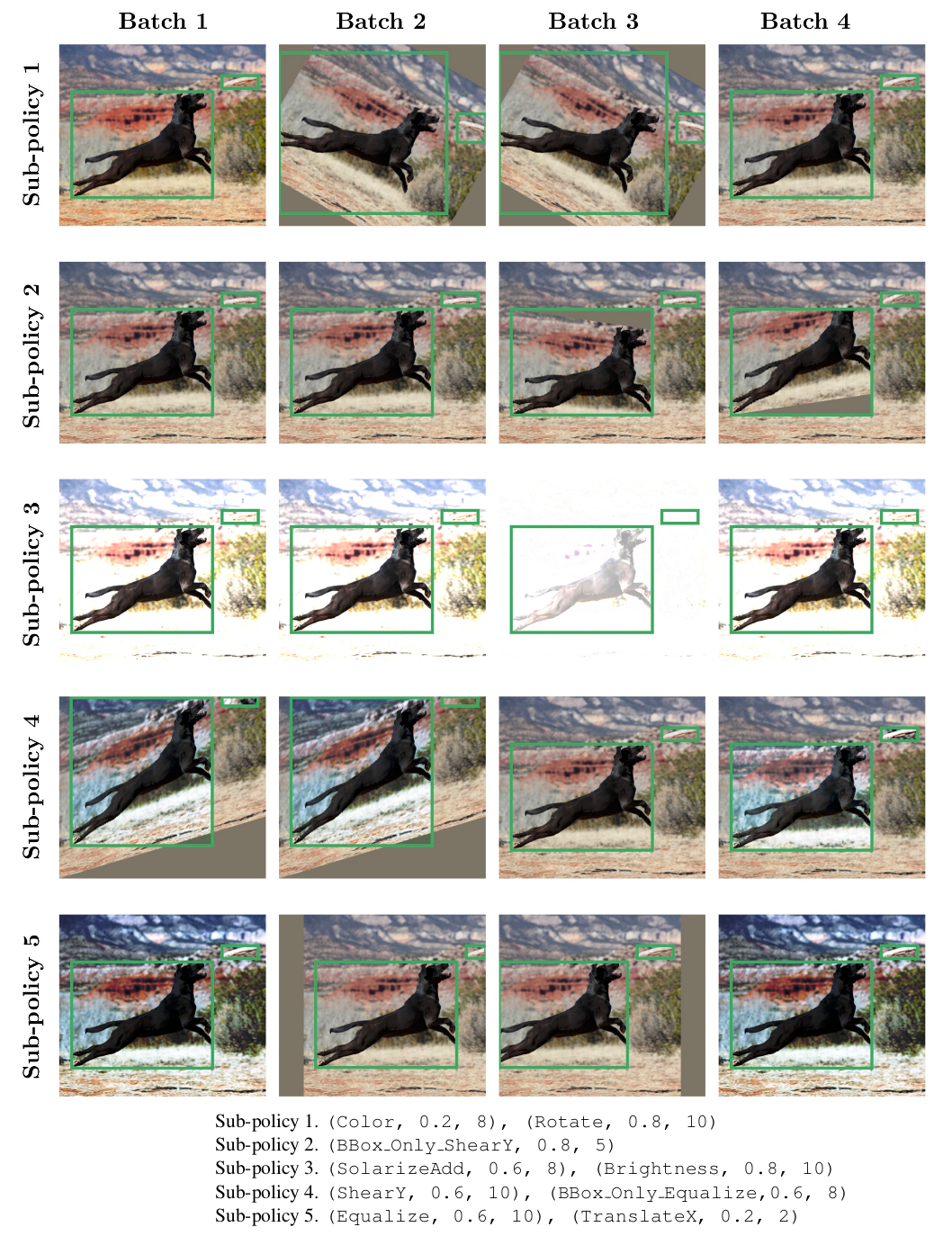
Implementation
They train an RNN with proximal policy optimization(PPO) as a reinforcement learning agent that outputs an optimal policy. The RNN is unrolled for 30 steps which correspondents to 2 operation for 5 sub-policies with each operation having three parameters to determine: type of operation, magnitude and probability. They train the model by choosing a subset of 5k images from COCO. The reward for the controller is a held-out validation set of 7392 images of COCO. The RNN controller is trained over 20k augmentation policies employing 400 TPUs over 48h.